
- Understanding Docking Station Power Distribution
- Fixed Power Delivery Docking Stations
- Dynamic Power Docking Stations
A docking station is a valuable addition to any desktop setup, providing video, data, and power—with power being one of the key benefits enjoyed by users. Docking stations offer a convenient one-stop-shop for all your device charging needs, but with the varying options available, how do you know which type of docking station is right for you? In this article, we will explore dock power delivery, the differences between fixed power delivery and dynamic power delivery, and the benefits that each can provide.
Understanding Docking Station Power Distribution for Optimal Device Charging
Docking stations have evolved to meet the diverse power needs of modern devices. They feature a range of I/O ports, each capable of delivering distinct levels of power, making them suitable for charging everything from small peripherals to laptops. Below, we detail the capabilities of each port type and explain how docking stations adapt their power delivery to meet the needs of different devices, including laptops.
Docking Station Port Power Capabilities:
-
4.5W Ports (5V/0.9A)
Ideal for low-power devices such as thumb drives, mice, keyboards, wireless trackballs, webcams, and wired headsets. -
7.5W Ports (5V/1.5A)
Suitable for slightly higher power devices, including SSD hard drives, phones, and LED desk lamps. -
15W Ports (5V/3A)
Designed for charging higher-power USB-C® devices like tablets, available on the latest USB-C® and Thunderbolt™ docks.
Laptop Power Requirements with Today's Docking Stations
One of the most critical devices that requires charging is the laptop. And, while many of today’s docks can deliver up to 100W power delivery based on the USB-C® PD 3.0 standard, it’s important to consider that the power delivery requirements for a laptop can vary depending on the laptop design, the task being performed and the battery level.
Laptop Power Use by Mode:
-
Hibernate Mode
Consumes approximately 1W—ideal for saving energy when the laptop is not in use. -
Idle Mode
Uses about 5W to 10W, typical for a laptop that’s on but not performing any tasks. -
Light Tasks
Activities like web browsing, word processing, or checking emails typically require 10W to 25W. -
Multimedia Use
Streaming videos or playing music can use about 20W to 50W. -
High-Demand Applications
Engaging in photo/video editing or using intensive software applications may increase power consumption to 30W to 70W, or even more, based on your laptop’s specifications.
When designing a docking station, engineers calculate the total power consumption of all the I/O ports in full usage along with the power consumption of the laptop in full usage (up to 100W). This calculation helps determine the appropriate power supply unit to be paired with the dock.
When the battery capacity is at a low level, for example, 10% battery remaining, high power delivery is required. Having 100W PD available at this time is beneficial for faster charging. However, once the battery is charged to 80%, some laptops will slow the charging to protect the battery life. At this point, only a lower power delivery, like 60W or even lower is needed depending on the laptop’s specifications.
Since power delivery needs vary by laptop design and usage, it’s helpful to understand the benefits of fixed power delivery and dynamic power delivery commonly seen on docking stations charging laptops to make informed decisions on what is best suited for your setup.
Fixed Power Delivery Docking Stations
Fixed power delivery docking stations provide a set amount of power to your laptop and connected devices, regardless of the connected device’s power needs.
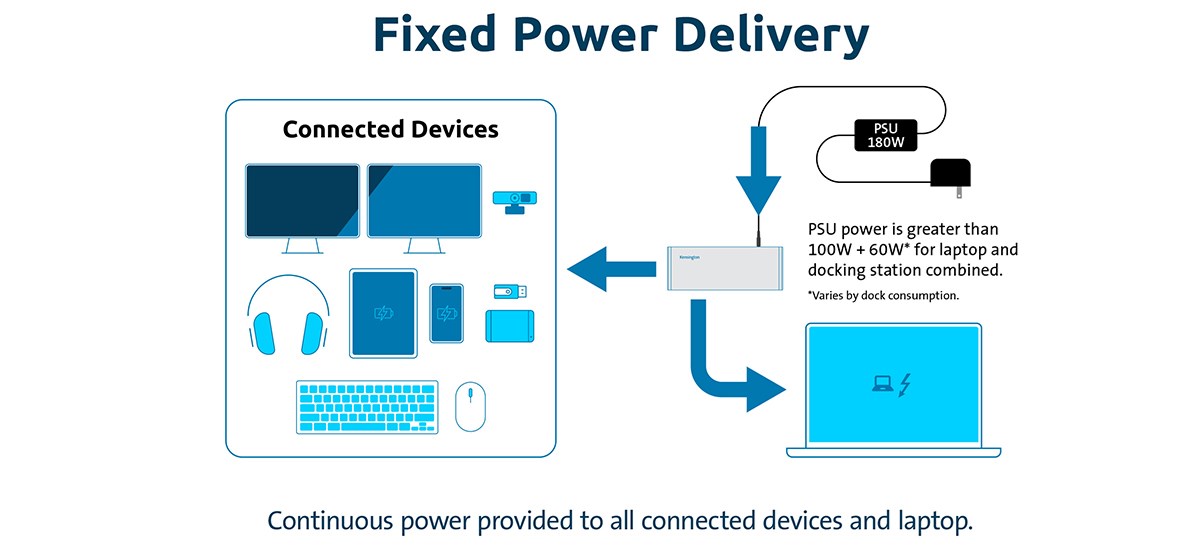
Image Title: Fixed Power Delivery
The Fixed Power Delivery method delivers a power supply unit (PSU) power of, for example, 180W to the docking station. The solid arrows represent continuous power drawing, providing power to the laptop and a group of connected devices, such as two monitors, a webcam, a headset, a tablet, a smartphone, a thumb drive, an SSD hard drive, a keyboard, and a mouse. The PSU power exceeds 100W + 60W* for the combined laptop and docking station. *The 60W varies depending on the docking consumption. Continuous power provided to all connected devices and laptop.
These types of docking stations offer a large enough power supply to guarantee the maximum power needed for laptop charging and operating the docking station, making them ideal for users who need a stable power source for their laptops. Here are some business scenarios where a fixed power delivery docking station is a good choice:
- Development Testing Labs: These teams often have multiple laptops, some of which have not been charged for extended periods of time, leaving laptop batteries at low levels (<5%). since the charging requirements are high, up to 100w of fixed power can be reserved for laptop charging while simultaneously charging other devices through the docking station's ports.>
- Designers and Videographers: Some software applications or laptops with discrete graphics consume high power (70W or higher). Since the power usage is high, up to 100W of fixed power can be reserved for heavy power usage while simultaneously charging other devices through the docking station's ports.
- Business Professionals: For users who frequently attend meetings or give presentations without time to charge between events, their battery life may be consistently low. In such cases, the faster charging feature of fixed power delivery becomes helpful to quickly replenish the battery.
Kensington's fixed power delivery docking stations are compatible with a wide range of Windows laptops and MacBooks, providing a convenient solution for device charging and data transfer.
Dynamic Power Docking Stations
Dynamic power docking stations provide power to your laptop and connected devices based on the device's power needs. These types of docking stations are more flexible than fixed power delivery docking stations.
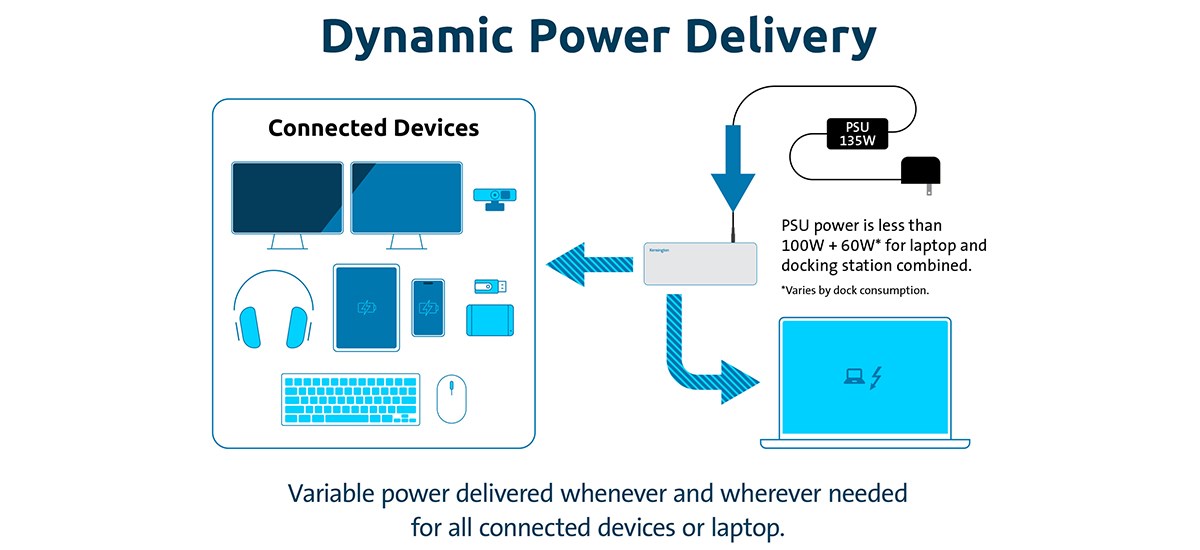
Image Title: Dynamic Power Delivery
The Dynamic Power Delivery method supplies a power of, for example, 135W to the docking station from the power supply unit (PSU). The two dashed line arrows represent variable power distribution, allowing power to be provided to the laptop when required or to a group of connected devices when needed. These devices may include two monitors, a webcam, a headset, a tablet, a smartphone, a thumb drive, an SSD hard drive, a keyboard, and a mouse. The PSU power is less than 100W + 60W* for both the laptop and the docking station combined. *The 60W varies depending on the power consumption of the docking station. Variable power delivered whenever and wherever needed for all connected devices or laptop.
Dynamic power docking stations are ideal for users who need a flexible power source that can accommodate different power needs. Here are some business scenarios where a dynamic power docking station is a good choice:
- Business Professionals: For users who keep their laptops charged or can connect to power more frequently, their laptop battery typically remains above 80%. In such cases, both the laptop and the devices connected to a dynamic power docking station receive sufficient power for charging purposes. Dynamic power also works well for users who only connect to lower power peripherals, such as mice and keyboards, since more power can be allocated to laptop charging.
- Commercial Laptop Users: For users of commercial laptops, such as ultrabooks and other thin-and-light laptops, these devices typically have lower power requirements (45W to 60W) and prioritize portability and energy efficiency. Even for laptops that require higher power (65W to 90W), dynamic power delivery will eventually charge both the laptop and connected accessories as needed, when needed.
Kensington's dynamic power docking stations currently offer up to 96W of power, with plans for up to 100W in development, and use dynamic power delivery technology to provide the optimal power output for your specific device. This ensures that your laptop receives the power it needs to operate at its maximum potential. In addition, dynamic power docking stations can be less expensive than their fixed power counterparts and offer the additional cost benefit of more efficient use of energy. Dynamic power docking stations are also compatible with a wide range of Windows laptops and MacBooks, making them a versatile solution for device charging and data transfer.
Which is Better?
Both fixed power delivery and dynamic power delivery docking stations are great choices for powering laptops and connected devices. The best choice is the one that works for your setup and working conditions. Here are some additional items to consider when deciding which will best support your needs:
Fixed Power
- Pros: 100W is consistently reserved for the laptop, ensuring sufficient supply during any demanding usage scenarios involving both the laptop and connected devices.
- Cons: Bulky power supply unit takes up valuable desktop space and may provide more power than needed since most commercial laptops only require 45W to 60W.
Dynamic Power
- Pros: Compact power supply unit saves space on the desktop. In addition, the power usage is more efficient.
- Cons: Not ideal for gaming or workstation laptop users since high-performance laptops require higher power consumption for optimal performance.
Conclusion
Choosing the right docking station hinges on understanding your specific power needs. Whether your priority is the stable, consistent supply of a fixed power delivery dock or the adaptable, efficient nature of a dynamic power delivery dock, the key is to assess your typical device usage and power requirements.
Kensington offers a wide range of docking stations that cater to diverse needs, from high-power devices to energy-efficient setups. Making an informed decision will not only optimize your desktop setup but also enhance your overall productivity and device management.
Find the perfect solution for your device charging and data transfer needs.